Different Types of Knitting Machines and Knitting Elements in Textile Industry
Types of Knitting Machines
Knitting Machine
The knitting machine frame is normally free-standing and either circular or rectilinear according to the needle bed shape providing the support for the machine mechanisms. The machine control and drive system coordinate the power for the drive of the devices.
The yarn supply consists of the yarn packages or beam accommodation, tensioning device, yarn feed control, and yarn feed guides. The knitting system includes the knitting elements, their housing, drive, and control, as well as associated pattern selection, and garment length control device The fabric takeaway mechanism includes the fabric tensioning, wind up, and accommodation mechanism.
The quality control system includes stop motion fault detectors, automatic oilers, and wind removal system
Types of Weft Knitting Machines
There are mainly two types of weft knitting machines.
1. Flat Knitting Machine
- V-bed Rib Machine (collar and cuff)
- Flatbed purl or Links Machine
2. Circular Knitting Machine
A) Large Diameter circular knitting machine
a. Single jersey circular knitting machine or single knit c.k.m
b/ Double jersey c.k.m or double knit c.k.m
- Circular rib machine
- Circular interlock machine
B) Small Diameter circular knitting machine
- Single cylinder
- Double cylinder
- Dial cylinder
Knitting Elements
Stitch: Stitch is the smallest dimensionality stable unit of all knitted fabrics. It is composed of -
- Head
- Two sides of a limb or legs
- Feet
Stitch length is the average length of yarn in a knitted stitch. It is sometimes called loop length.
Course Length:
Course length is the straight length of yarn of a course. In weft-knitted fabric, a course of loops is composed of a single length of yarn.
The course length of yarn is measured by the course length tester.
S.L = Course length/ No. of needle knitting in a machine
Stitch Density:
Stitch density is the straight length of needle loops in a measured fabric area and not the length of yarn. It is the total no of needle loops in a given area such as a square inch
G.S.M = Gram per square meter
Relation:
- When stitch length is higher, stitch density is low i.e. G.S.M is low
- When stitch length is insufficient, Stitch density is high i.e. G.S.M is high
Machine Gauge:
The machine gauge is referred to as the number of needles per inch. It is denoted by "G"
Needle:
The needle is the principal element of a knitting machine. It is a thin metal bar. During yarn feeding the hook releases the retained old loop and receives the new loop which is then enclosed by the theme.
Types of Needle:
The needle of knitting machine mainly consists of three types. They are
- Latch Needle
- The Bearded Needle
- The Compound Needle
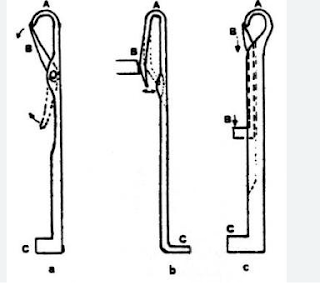 |
| Fig: Types of Knitting Needle |
Cam: Cam is the device that converts the rotary motion into a suitable reciprocating action for the needles and other elements.
 |
| Fig: Knitting Machine Cam |
Classification of Cam:
There are mainly two types of cam used in knitting
1. Circular Engineering Cam (for weaving)
2. Angular Knitting Cam (acts directly on the butts of the needle)
a. Raising cam
- Knit cam
- Tuck cam
- Miss Cam B. Guard cam
c. Stitch cam
d. Up-through cam
Sinker:
Sinker is the second primary element of a knitting machine. It is a thin metal plate with an individual operating approximately at right angles from the hook side of the needle bed between the adjacent sinker shape and size.
The function of Sinker:
- Loop Formation
- Holding down the loops
- Knocking over the loops
Figure of Three Types of Sinker:
Knitting Machine with Revolving Cylinder:
- Single jersey circular knitting machine
- Circular interlock machine
- Circular rib machine
Knitting Machine with Stationary Cylinder:
- V-bed rib machine
- Flatbed purl machine
- Single cylinder
- Double cylinder
- Single cylinder and dial
Basic Weft Knitted Fabric Structure:
- Plain structure (face side and back side are different)
- Rib structure (both sides are same)
- Interlock structure
- Purl structure
The Machines Where the Plain Structure is Formed:
- Single jersey circular knitting machine
- Single cylinder
- V-bed rib (front or back bed)
- Flatbed purls (single bed)
- Double-cylinder circular knitting machine (bottom cylinder)
The Machine Where the Rib Structure isis Formed:
- V-bed rib machine
- Circular rib machine
- Double cylinder
- Cylinder and dial
Hosiery Knitting Machine
A knitting machine for the production of hosiery. Most of them are small-diameter latch needle circular knitting machines.
Features of Hosiery Knitting Machine:
1. According to the rotation of the cylinder
- Grishold hand-type knitting machine/ stationary circular type
- Revolving cylinder with holding down sinker.
2. According to the number of needle bed:
- Single cylinder
- Double cylinder
- Cylinder and Dial
Hosiery Machine Gauge:
The Hosiery machine gauge is expressed as the diameter and total no of needle
Tricot Warp Knitting Machine:
Warp knitting is a process of forming fabric by knitting where loop formation takes place on a vertical basis and enjoyable loops take place along the length of fabric or wales-wise. basis. The machine where this type of knitting takes place is called a warp knitting machine. This machine is very much diversified and versatile.
Types of Warp Knitting Machines:
In general, warp knitting machines can be classified into three types.
- Tricot
- Rashcel
- Crochet
- Warp Beam: It has two warp sheets (top and bottom) to ensure uniform feeding and tensions
- Warp Tension Rail: To keep the warp sheet under uniform tension.
- Comb: Two combs to distribute warp uniformly and to individualize warp thread.
- Guide and Guide Bars: It has two guide bars, front and back guide bars. Guides are used to guide warp.
- Compound Needle and Needle Bar: To intermesh loops and knock over the new loop through the old loop and to accommodate needles.
- Sinker: Holding down the fabric, old loop, and support the fabric.
- Pattern Drum: Provides shogging action, contains chain links, and links are connected by a chain.
- Connecting or Push Bar: To push the guide bar.
- Rocker Shaft: Provides swinging motion
- Temple(2 rods): To control the width of the fabric
- Take Down Roller: To withdraw knitted fabric from the knitting zone. Control 3 tension rollerise above other.
- Take Up Roller: To collect the fabric.
Flat Bed Knitting Machine
Flad bed knitting machine was first demonstrated by Gssoc Wixon Lamb (American). Flat bed knitting machine is of two types
- V-bed rib machine
- Flat bed purl or link machine
Features of Flat Bed Knitting Machine
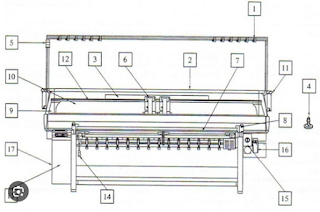 |
| Fig: Flatbed Knitting Machine |
- Two stationary needle beds in inverted v formation
- Latch needle is used
- Angular bi-directional cam system is used
- Seperate cam system for each needle bed
- Two cam system are linked by a bridge
- Carriage also contain a yarn carrier
- Fabric produce finer to coarser gauge
- Stitch length variable is available
- Trimming, edging collar, fully fashionable knitted garments are produced
The Function of Flatbed Knitting Machine Parts:
- Fabric Comb: Hold the fabric and lock the fabric coarse
- Needle Bed: Carrier needles
- Latch Needle: Loop formation
- Cover Plate: Romove the faulty needle from the needle bed.
- Security Spring: Helps to select the needle.
- Cam Carriage: Carry and traverse the cams
- Latch Opening Brush: Fully opens or closes the needle
- Guide Rail: By bearing cam carriage moves along it.
- Yarn Carrier: Carry yarn
- Feeder: To feed yarn
- Lever: Two types of lever:
- Rocking Lever: Rock the back needle bed.
- Gap Opening Lever: To adjust the gap between front and back bed.]
- Cymbol Tensioner: To provide tension to the yarn
- Selectors: To select colored yarns
- Dead Weight: Attached with fabric comb
- Cam System: Four types of cam system
- 1 Guard cam for each bed
- 2 Cardigan cam for each bed
- 2 Stitch cam for each bed
- 2 Raising cam for each bed.
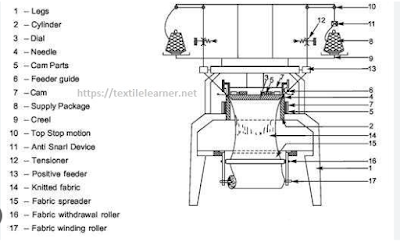
Circular Knitting Machine
Circular knitting machine is widely used throughout the knitting industry to produce fabric. This machine can be built in almost every reasonable diameter and the small diameter up to five which are used for water. In circular knitting machines, the rotation of the needle cylinder drives the needle through the knitting channel in a vertical up and down movement
Function of Circular Knitting Machine Parts:
- Latch Needle: Used to form loops
- Cam: Use to convert rotary motion into reciprocating action for needle and other elements. To form knit, tuck and miss loops
- Sinker: Used to form loops, holding down the loops and knocking over the loops
- Feeder: It supplies yarn to needle
- Knot Catcher: To find any faults in yarn
- Yarn Tensioner: It provides proper tension to yarn for knitting
- Inlet & Outlet Stop Motion: It stops the machine when the yarn is break
- Yarn Guide: It helps the yarn to feed in the feeder
- Timing Belt/ Tooth Belt: It helps the machine to stop immediately
- VDQ Pulley: Used to control the stitch length of the fabric
- Driving Handle: To drive the cam for transport
- Cover Plate: To cover the machine and prevent from dust
- Cam Selector: To select particular cam for different design of fabric
- Stitch Length Regulator: To control the length of stitch
- Fabric Comb: To set the first course into the needle
- Comb Wire: To feed the yarn into the fabric comb
- Dead Weight: To maintain the uniform tension of fabric.
V-Bed Flat Knitting Machine:
Flatbed Knitting machine produces flat pieces. It cannot work purl stitches or garter stitch automatically. A flatbed knitting machine comprising a flat elongate bed on which is retained a plurality of parallel, latchable, needles equally spaced alogh the length of the bed and each movable relative to the bed in a direction lengthwise of the needles and transverse of the bed length.
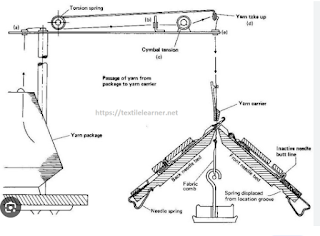 |
| Fig: V-bed Flat Knitting Machine |
The Function of V-bed Flat Knitting Machine
- Creel: To store the yarn package
- Yarn Guide: To give particular path of yarn
- Yarn Tensioner: To give proper tension for knitting
- Feeder: To feed the yarn to the needle
- Needle: To form loops
- Brush: To open the latch and clean the needle
- Needle Bed: To hold and stores the needles
- Cam: To convert rotary motion to reciprocating action for needle and other elements and to form different design of fabric
- Cam Carriage: To house the cam
- Cylinder: Used to store the needles, cams and sinkers
- Sinker Ring: Sinkers are placed on sinker cam in the sinker ring
- Needle Bed: Where all needles are placed in a decent design
- Needle Detector: It detects any type of needle faults
- Take Up Roller: Used to take up the fabric from cylinder
- Fabric Roller: Cloth is wound on this roller
- Fabric Detector: Used to find any faults of fabric
- Feeder Ring: Where all feeders are placed together
- Expander: To control the width of fabric
- Creel: To contain yarn package
- Tube: Used to pass the yarn to the feeder unit
- Adjustable Fan: To remove lint, hairy fiber from yarn and others










Comments
Post a Comment